Fence Bracing: Materials, Methods, and Types for Strong and Durable Fences
Introduction
When it comes to building a fence, the bracing plays a vital role in ensuring its stability and longevity. With various materials, methods, and brace types available, it's important to consider factors like strength, durability, and ease of construction. In this article, we will explore different aspects of fence bracing and provide insights to help you make informed decisions for your fencing project.
Material Considerations
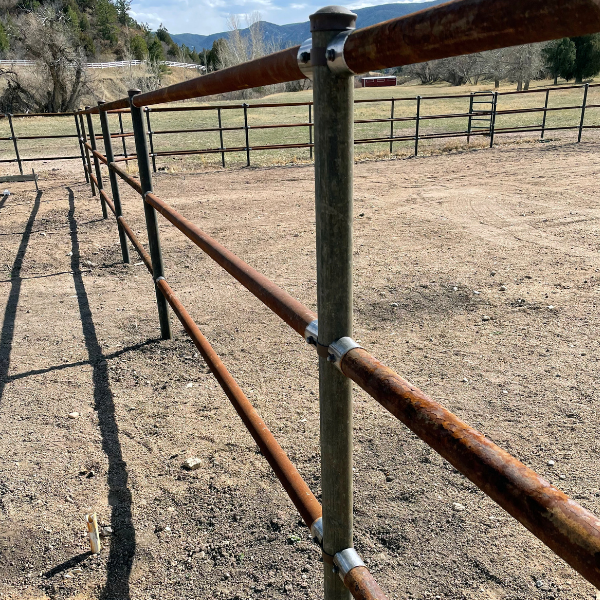
Wood posts are prone to moisture absorption, warping, and rotting over time. On the other hand, steel pipe posts offer exceptional strength, resistance to rot and warping, and increased durability. Galvanized or painted steel pipe posts further eliminate rusting, providing a brace that can outlast wood by decades.
Post Setting Methods
Wood posts require larger holes or pounding. Pounding sometimes results in splintered or broken posts in hard ground. In contrast, steel pipe posts are easier to drive and can be set to a greater depth. Concrete is typically used for setting steel pipe posts when holes are dug, ensuring enhanced stability compared to hand-tamped soil for wood posts.
Construction Methods
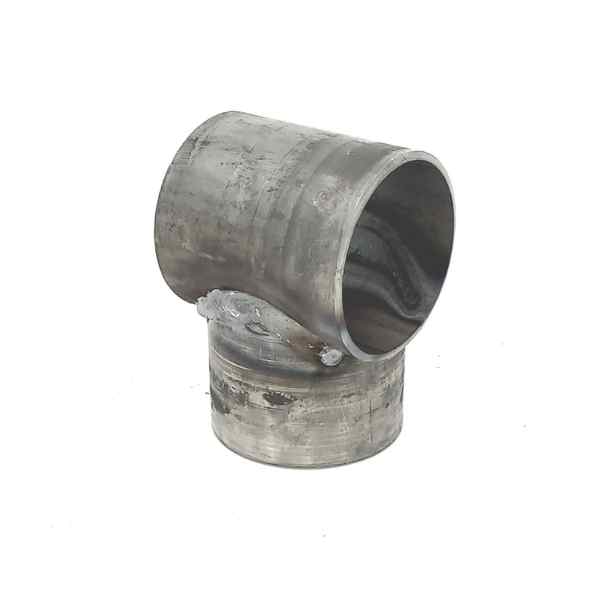
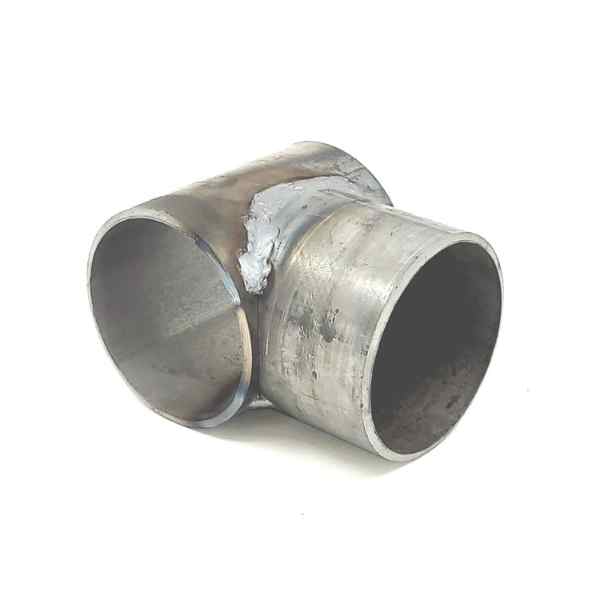
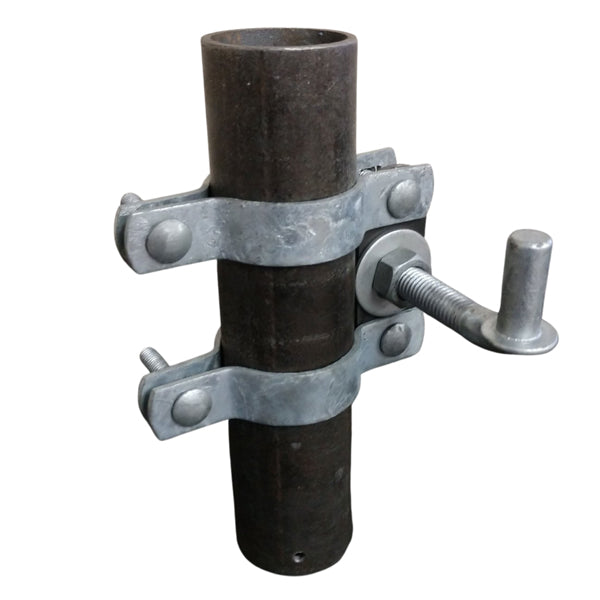
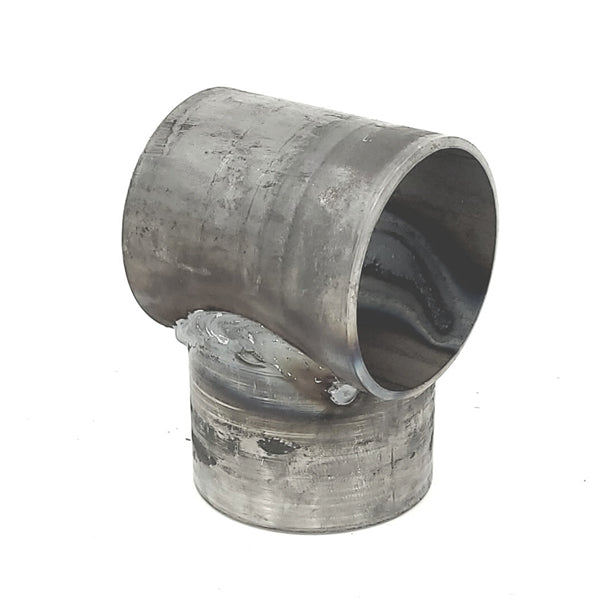
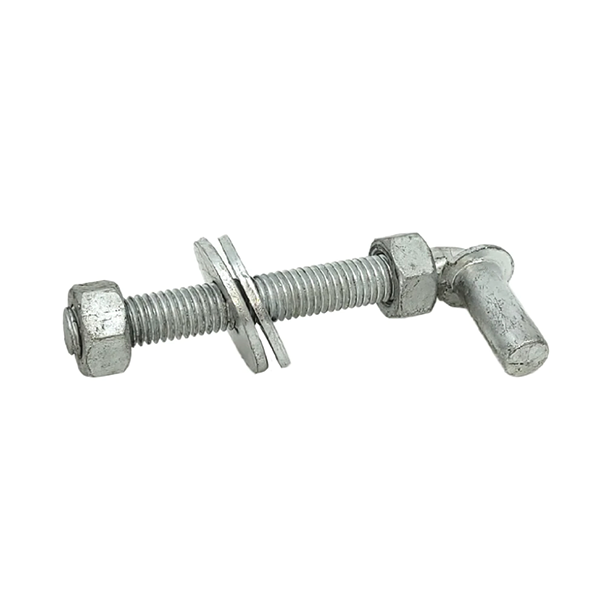
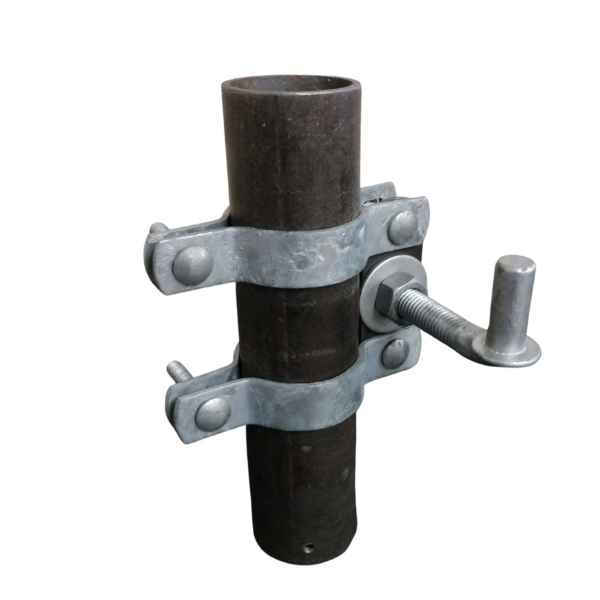
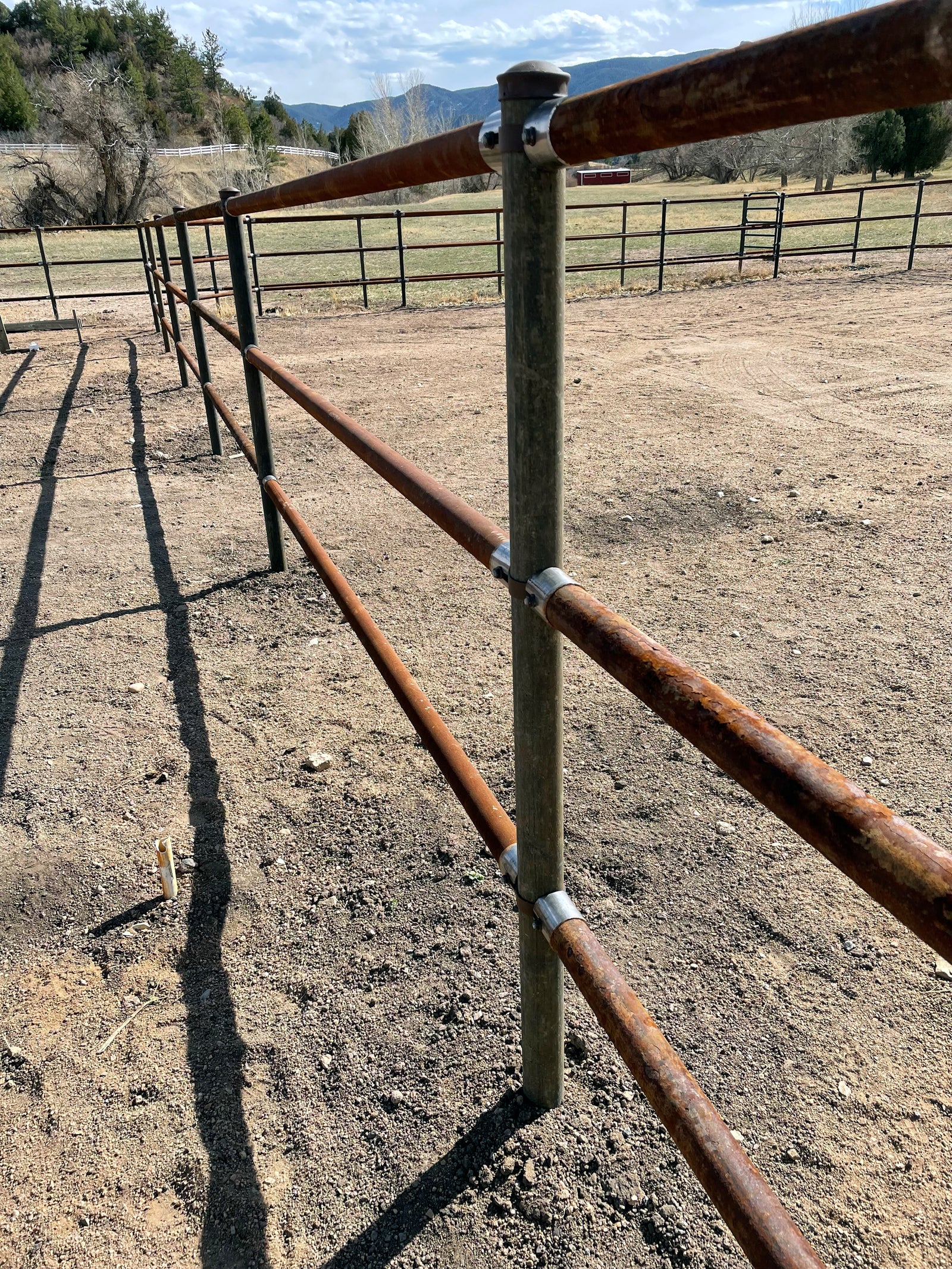
Wood braces are commonly joined together with pins or mortised. Mortising is time-consuming construction. Wire bracing is commonly used in H braces to prevent leaning, but it adds complexity and time. Steel pipe posts can be joined by welding or utilizing no-weld systems. No weld systems offer faster and simpler construction than welding. No-weld systems also eliminate fire hazards and enable remote construction.
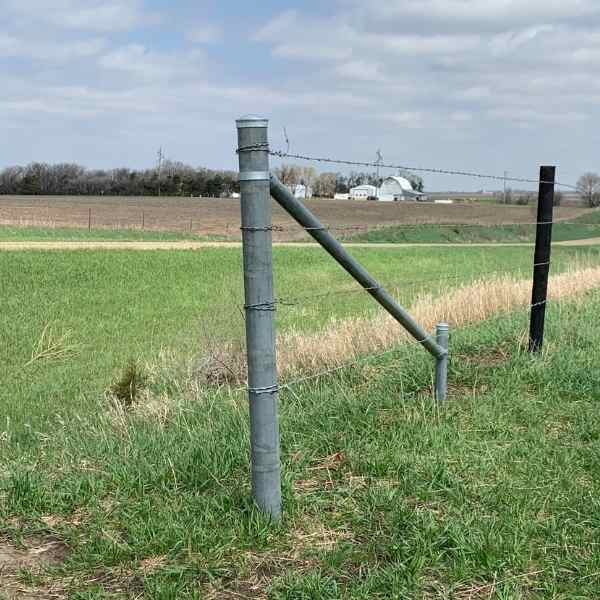
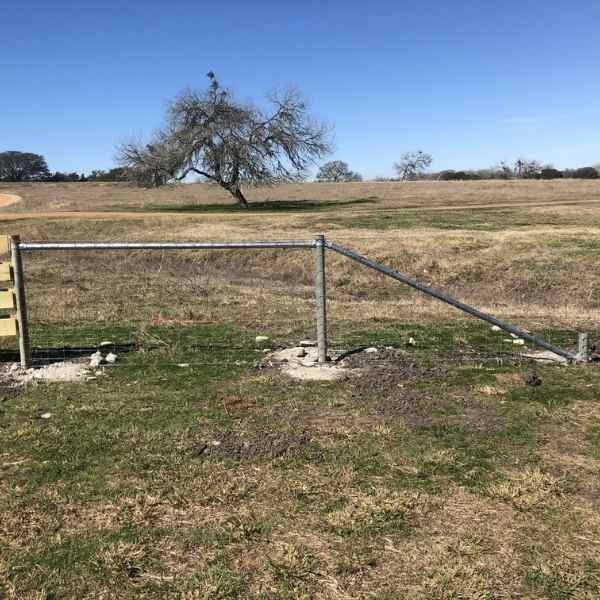
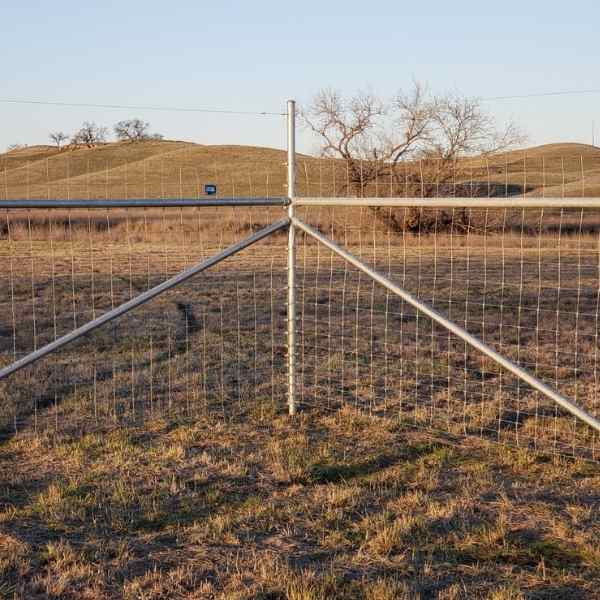
Brace Types
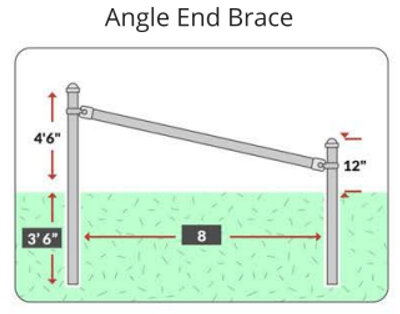
H braces are widely used, but angle braces should be considered superior due to the physics involved. Angle braces create a stronger triangle, transferring pressure directly to a ground-level post under compression. In contrast, H braces transfer pressure at a higher point, potentially pushing the bracing post and requiring wire tension adjustments over time. The wire brace used in H braces is the weak link in a more complex and weaker brace design. Also angle braces offer advantages in terms of material efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Conclusion
While debates about fence bracing techniques will continue, advancements in understanding continue to shape our approach. By embracing new materials, methods, and brace types, you can create fences that are stronger, longer-lasting, and easier to build. Consider the advantages of steel pipe posts, efficient construction methods, and the superiority of angle braces. By prioritizing strength, durability, and ease of construction, you can achieve a fence that stands the test of time.
























Leave a comment (all fields required)